Biodiversity refers to the variety of life found on Earth, including the different species of plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms, as well as the genetic diversity within these species.
Read MoreAnimal migration is one of nature's most extraordinary phenomena. Many species undertake long journeys in search of better resources, breeding grounds, or favorable climates.
Read MorePlay is a universal behavior observed in many animal species, from domestic pets to wild animals. While often seen as mere entertainment, play serves several important functions in the lives of animals.
Read More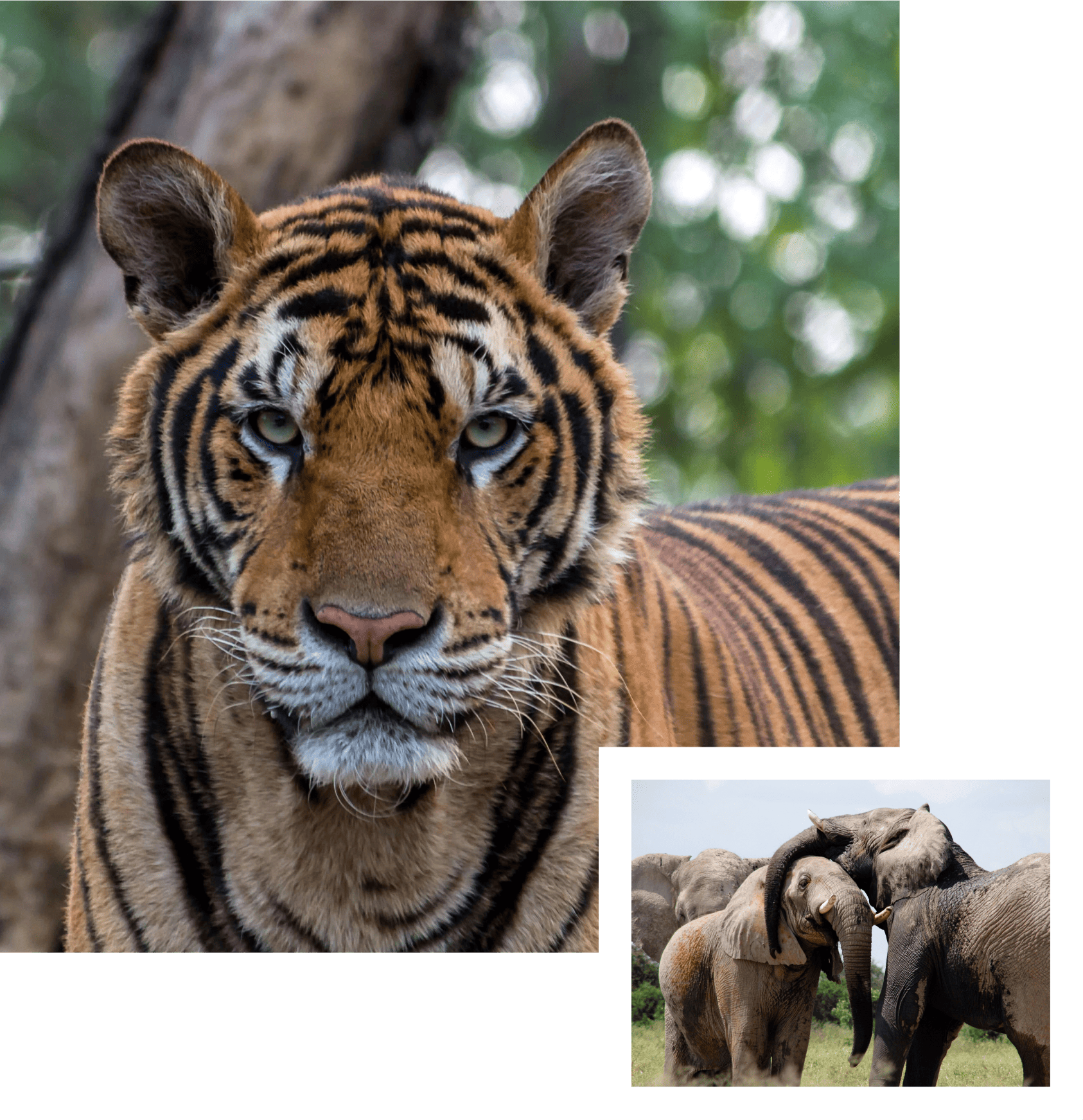
Many animals live in complex social groups where cooperation and hierarchy are key to survival. From wolf packs to elephant herds, these communities rely on teamwork for hunting, protection, and raising young.
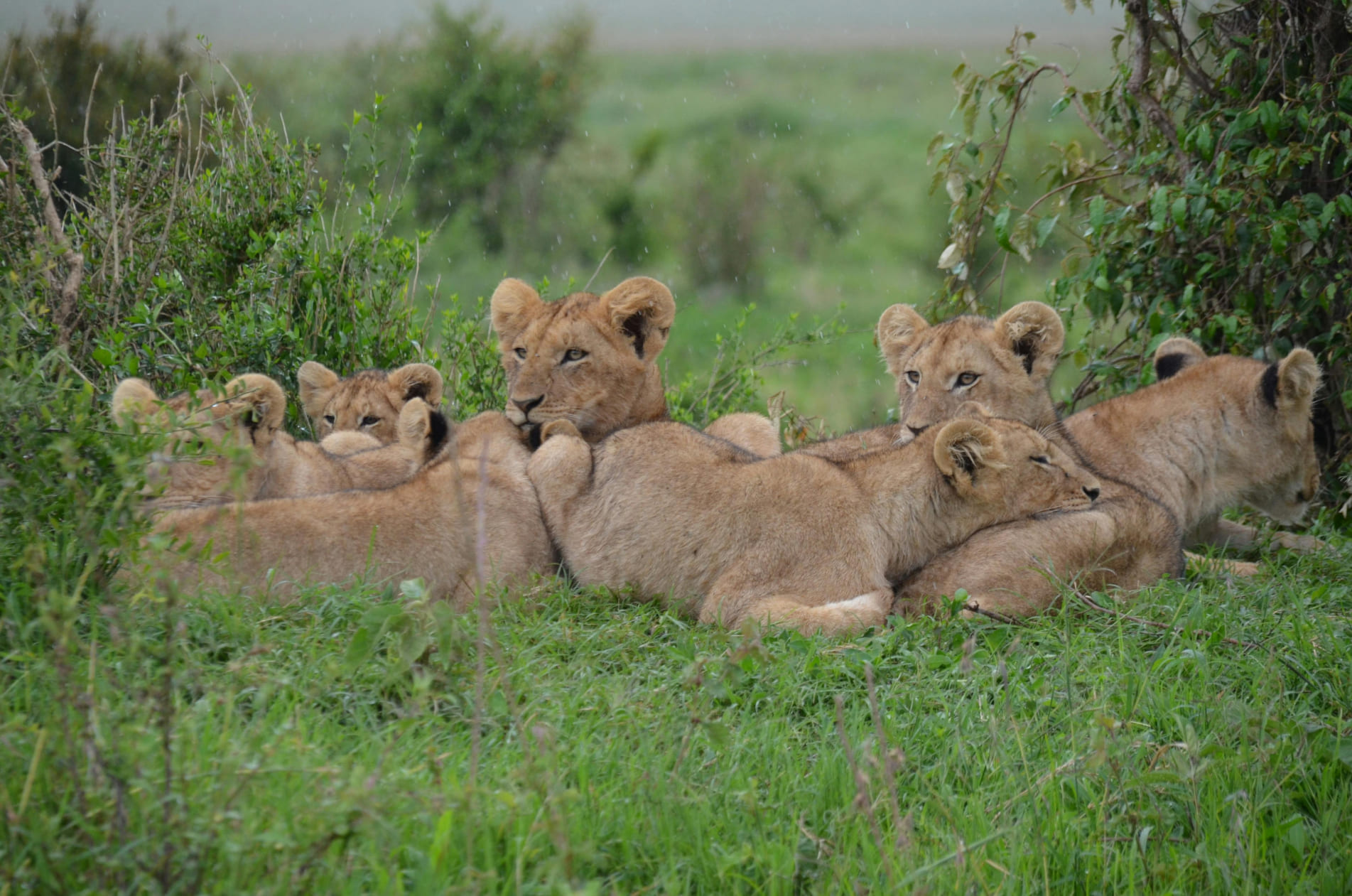


Carnivores, such as lions, wolves, and sharks, are at the top of the food chain. Their hunting behaviors control prey populations, keeping ecosystems in balance and ensuring that weaker animals do not dominate the landscape.

Amphibians, such as frogs and salamanders, are important indicators of environmental health. Because of their permeable skin, they are highly sensitive to changes in water quality and pollution, making them key species for monitoring ecosystem health.

Animals like birds, mammals, and insects help disperse seeds across vast distances. This process allows plants to colonize new areas, promoting biodiversity and the spread of various plant species in ecosystems.
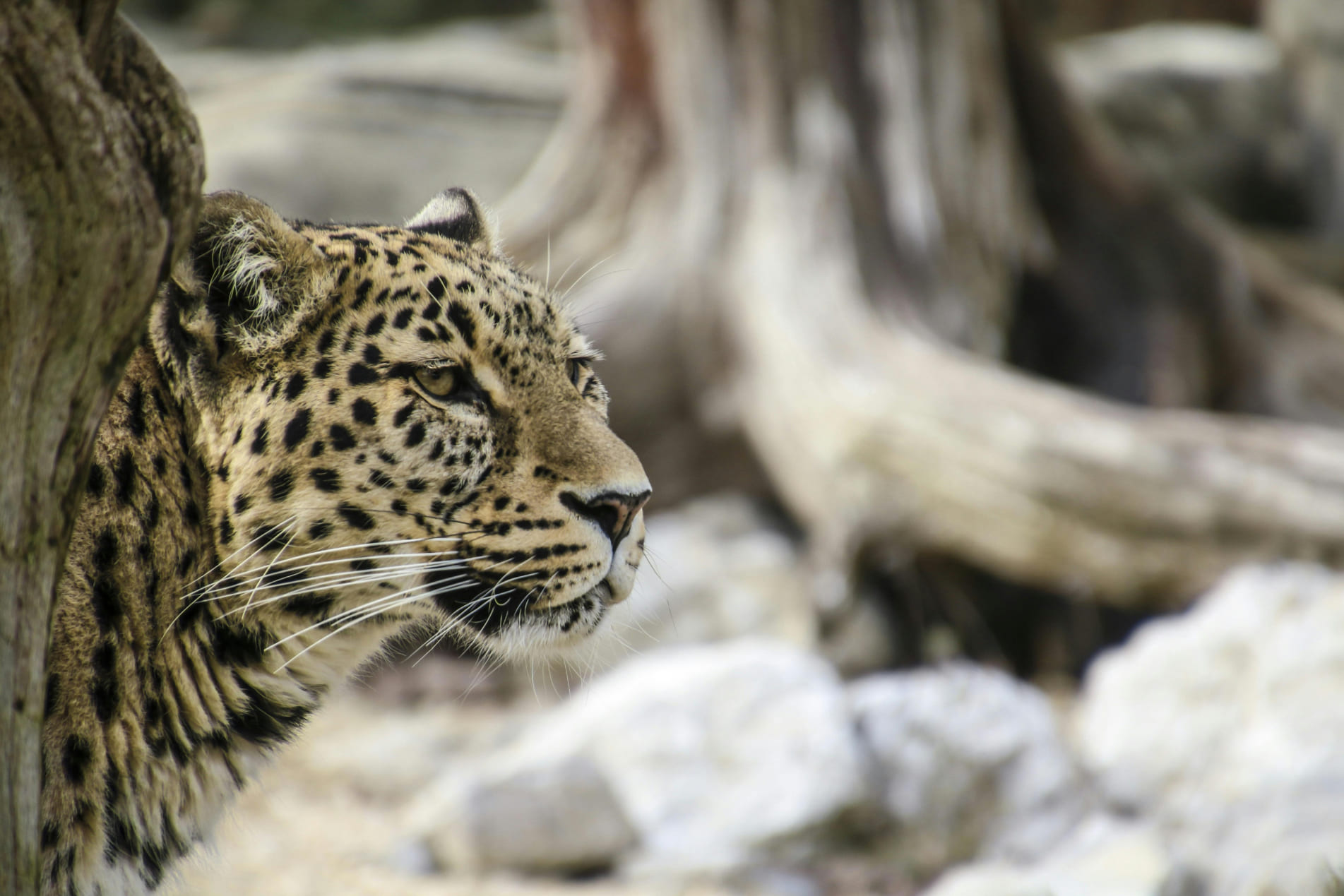

Invertebrates, such as spiders, worms, and mollusks, make up the vast majority of animal species. They play crucial roles in ecosystems, from aerating soil to controlling insect populations, and form the foundation of many food webs.
Some animals enter hibernation to survive cold winters when food is scarce. Bears, bats, and certain rodents slow their metabolism and lower their body temperature, conserving energy until conditions improve.
Many animals are capable of learning and adapting to their environments. Whether through trial and error, observing others, or mimicking behaviors, species across the animal kingdom demonstrate the ability to learn for survival.



Marine mammals like dolphins and whales are critical to ocean health. Their feeding patterns influence marine food webs, and their migration patterns provide valuable information for conservation efforts.